NEED FOR EARLY CARBON OPTIMIZATION
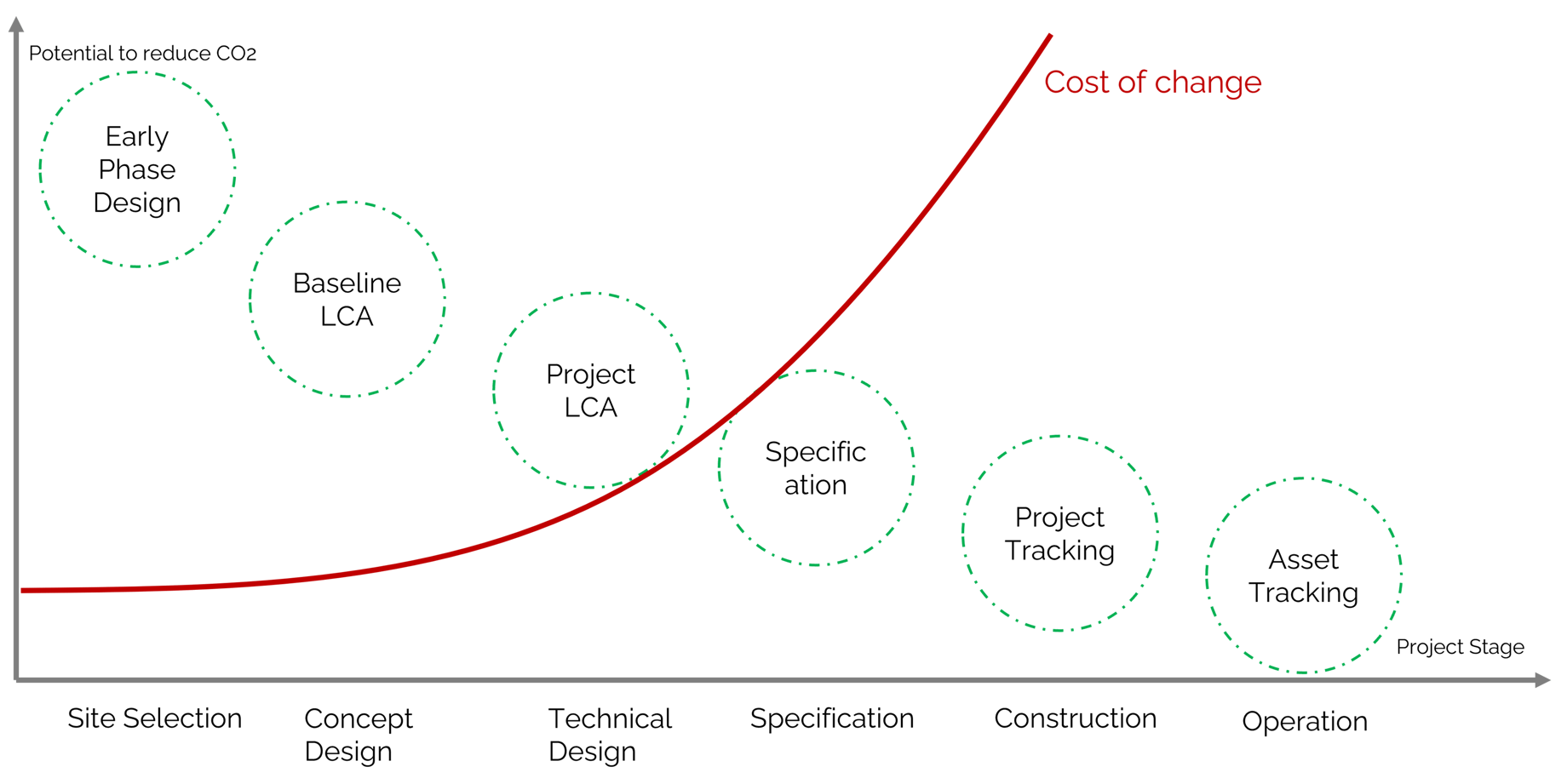
Optimizing carbon in various project stages
Conducting Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) helps to measure and reduce the environmental impacts of your building, achieve green building certifications, and comply with regulations. Depending on the objective, LCA can be performed during multiple stages of a project and can provide various advantages (refer to Table 1).| Project stage | Advantages of performing building LCA |
| Site selection stage |
|
| Concept stage |
|
| Technical stage |
|
| Specification stage |
|
| Post-construction |
|
LCA can be performed at multiple stages but if your goal is to achieve maximum embodied carbon reduction, you need to perform it when you have the maximum power to influence design and specification choices.
Strategies to reduce embodied carbon
The Carbon Neutral Cities Alliance (CNCA) has identified five different tactics that can be deployed to reduce carbon emissions(see Fig 1).- Redefine the solution: finding alternative ways to reduce carbon. For example, if a leisure time facility is underused, the problem may relate to public transport access as opposed to needing to rebuild or renovate the building.
- Refurbish existing assets: This reduces total materials use and can be a powerful decarbonisation strategy where it does not compromise energy efficiency. For example, renovations to increase usage efficiency in capacity, occupancy, or both.
- Reduce and Replace materials and structures by design and use lower carbon structures and materials where appropriate.
- Reuse products and materials, at end of life for additional uses for unused products from sites and for salvaged materials from refurbishments and demolitions
- Require low carbon products, for example specifying low carbon products while limiting and/or substituting the use of high carbon materials for lower impact ones.

During the early design stages, there is greater flexibility to influence all of the steps to reduce embodied carbon. During this stage, design teams have the capability to assess different solutions, structural frames, locations, material choices, and many more.
Identifying the stage with the highest potential
Cost considerations

Certification schemes and regulations that promote early carbon optimization
| Schemes | Description |
|
|
|
/living-building-challenge-card-fourth-65cef487ba554.webp?width=160&height=90&name=living-building-challenge-card-fourth-65cef487ba554.webp)
Living building challenge |
|

LEED |
|
TOOLS THAT HELP YOU WITH EARLY CARBON OPTIMISATION
Challenges while performing early carbon assessments
The main challenge when we want to perform an LCA at the early design stage is the lack of information, whether this is the material specifications, quantities, or even the specific material impact information.
Since the goal of an early stage LCA is to obtain a general overview of the anticipated carbon emissions, it can be acceptable to use previous projects’ information and extrapolate accordingly. However, such a methodological approach would entail dangers because it makes it difficult to assess multiple design options (i.e., the quantities required for a concrete frame are not the same when assessing timber frames, etc).
Listed below are some potential tools to help you overcome these challenges.
Create baseline
Carbon designer
Carbon designer is an early design tool that allows you to get a Bill of materials (BOM) without needing a design. It is a shoebox analysis model but useful for the early design stage.
Benefits
- Early Design Tool
- Uses local average data
- Obtain BOM without needing a design
- Minimal amount of information required
- Perform cost vs carbon analyses
Features
- Create baselines with minimum data such as GFA, country/region, building type, and number of floors
- Allows for optional choices such as underground floors, soil conditions, structural solutions etc
- Templates allow you to reuse your baselines in any number of projects quickly and easily
- Quick and easy visual comparison by rapidly making variants by changing between pre-defined building structures or relevant material choices
- As only very limited background information is needed to start, the tool can be used already in early design stages and target setting but it can also support detailed options and creation
- The modelled building can also be saved to any of our LCA calculation tools

Typical workflow
- Enter basic information (size, ref building, service life)
- Select your building type
- Define the scope of the analysis (select the building parts you want to work with)
- Choose your baseline structural frame (concrete, steel, timber, etc)
- Review and calculate the final geometry
- Review and amend material quantities
- Review your first results
BIM tools
Rhino and grasshopper integrations
One Click LCA has developed integrations with Rhino and Grasshopper to help design teams implement carbon assessments from the earliest stages. The Rhino integration is designed to allow users to directly assign materials to the drawn layers and eventually get a result for their project. This allows design teams to quickly identify where the carbon hotspots might be located in the final design and tackle them from early on.

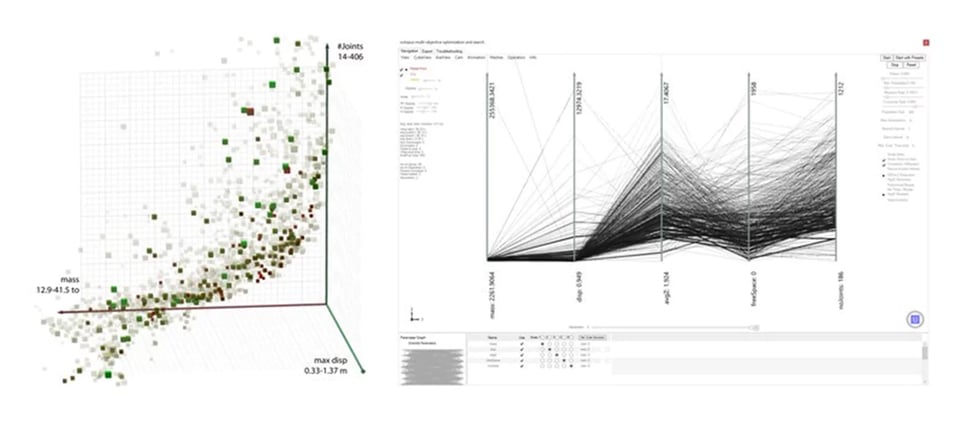
Fig 3. Iteratively optimizing your design using parametric tools
Benefits
See in real-time how changing your parameters affect your project’s embodied carbon.
Typical workflow
- Set up your initial script
- Choose the materials you want to use
- Run and LCA within grasshopper
- See in real-time how changing your parameters affect your projects embodied carbon
Combine grasshopper and carbon designer to develop full-scale buildingsEarly design in GH (only column, walls), you can add this to OCL and using CD you can fill in the gaps and have a full building LCA done |
Carbon Experts Newsletter
Industry news & insights — straight to your inbox
Want to learn more?
Panu Pasanen • Feb 20 2024
Asha Ramachandran • May 02 2024
Billy Lusk • Jul 03 2024
Aileen Carroll • Aug 07 2023
 GLA London Plan
GLA London Plan