Guide
BIM & LCA — Autodesk Revit & One Click LCA
Comprehensive guide for integrating BIM & LCA with One Click LCA Autodesk Revit integration, covering everything from setup to advanced analysis.
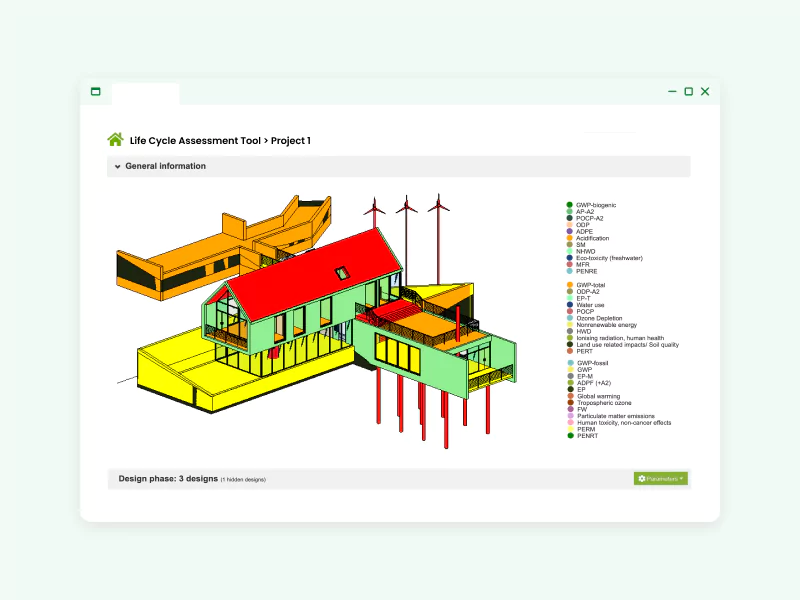
About the guide
- A comprehensive guide on One Click LCA — Revit integration, including installation and integration options.
- To improve practical LCA and BIM (Building information modeling) integration, with steps to establish
internal workflows. - Serve as a reference for plugin settings and data inputs.

Why integrate BIM & LCA?
- Integration of LCA with BIM enables accurate and comprehensive building
LCAs quickly using BIM models. - BIM models allow simulation of various design scenarios to compare
environmental impacts, aiding in selecting sustainable designs. - Improves team communication and collaboration by providing a unified
information source, reducing errors, and ensuring sustainable designs.
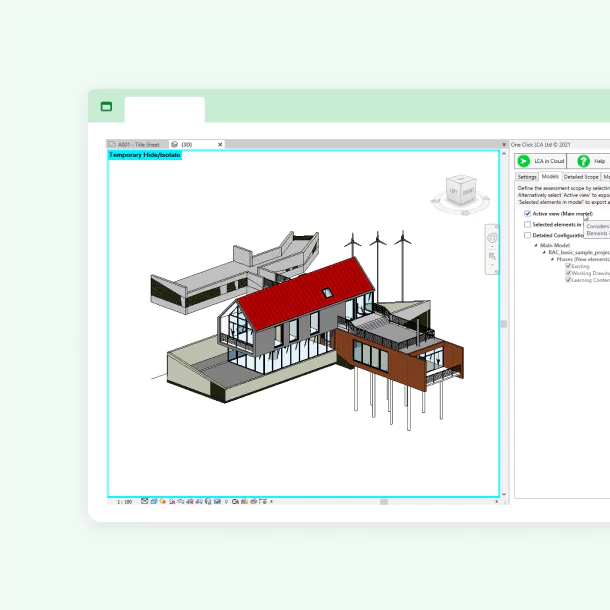
About Autodesk Revit
- Go-to BIM software for the AEC industry, Autodesk Revit, streamlines the
creation, visualization, and documentation of building designs. - Supports a broad spectrum of design and documentation tasks, from
architectural design to MEP and structural engineering, with advanced
tools for 3D modeling and data management.
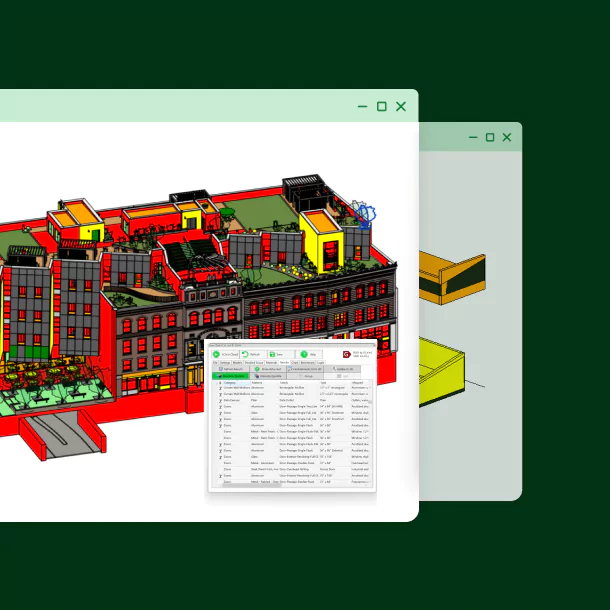
One Click LCA integration in Revit
- Extract relevant data (material names, categories, geometric data, units)
from Revit models for LCA. - Speeds up data input for 'building material' queries in One Click LCA, allowing direct work from Revit for complete LCA studies.
- Enables quick analysis of material choices for sustainability during the design process in Revit, without disrupting workflow.
- Integration assesses changes without altering Revit model geometry,
facilitating seamless integration and sustainability insights.
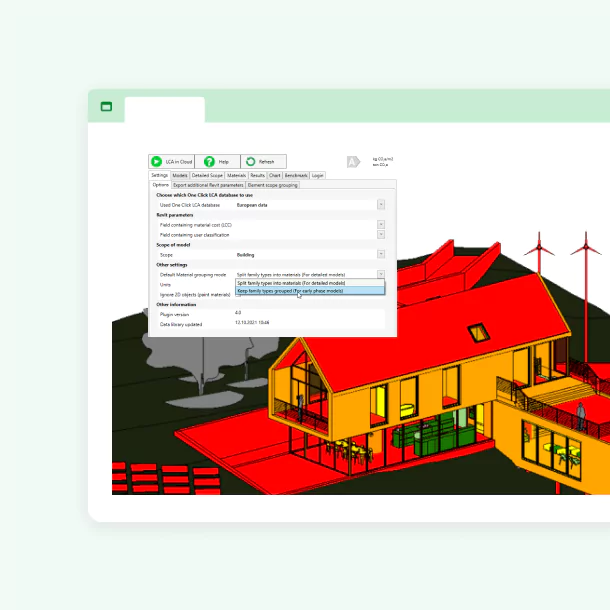
Streamline LCA process with the One Click LCA Revit tool
Watch our webinar on integrating Autodesk Revit with One Click LCA for construction and design professionals. Experts Becky Burns, Sophie Martin, and Kostas Koukoulopoulos discuss improving sustainability through efficient LCA processes.
Frequently asked questions
One Click LCA X Autodesk Revit plugin
How should I assess windows and doors?
Windows and doors are best assessed by keeping their family types grouped. This means you will get the overall projected window/door area instead of quantities of individual materials, e.g., glass, aluminum, PVC, etc. The window/door area must then be mapped with an EPD or generic data point that represents an entire window/door, including the panel and frame. This is a better option because the frames in windows and doors are often modeled as solid elements ignoring the hollow part of the profile is made of aluminium or PVC, and also because the glazing is typically modeled as a single, considerably thicker glass pane instead of two or three thinner ones for double and triple glazed windows respectively. More information on this topic can be found in Revit guide Paragraphs 7.2.3 and 7.2.4.
How should I assess hollow core slabs?
Hollow core slabs are best included in an LCA by using their area instead of the individual material quantities. This area must then be mapped with an assembly, EPD, or generic data point that represents the entire profile of this slab, including the concrete, the hollow cores, and the reinforcement. More information on this topic can be found in Revit guide Paragraph 7.2.1.
How should I assess composite metal decks?
Composite metal decks are best included in an LCA by using their area instead of the individual material quantities. This area must then be mapped with an assembly, EPD, or generic data point that represents the entire profile of this slab, including the concrete, the steel deck, and the additional reinforcement. More information on this topic can be found in Revit guide Paragraph 7.2.2.
How should I assess curtain walls?
Curtain walls are typically best included by using the area of the curtain wall panels and the length of the curtain wall mullions. In both cases, it might be best to map these two quantities with custom assemblies that accurately represent the panels and mullions. This is because, in many cases, curtain wall panels are modeled at a lower level of detail in Revit models, while curtain wall mullions might be modeled as solid elements, ignoring the hollow core of their profile, and might also include materials and elements that form part of the panel in reality. More information on this topic can be found Revit guide in Paragraph 7.2.5.
How should I use my Revit model for LCA if it is not detailed enough?
The level of detail of your Revit model should not prevent you from using it for LCA. Revit models with a lower level of detail can still be used by extracting the family type quantities instead of material quantities. These quantities can then be mapped with One Click LCA assemblies, e.g., the area of the external wall from Revit can be mapped with an external brick slip wall assembly in One Click LCA. This way, although it is probably too early in the design process to know the exact materials and thickness of these materials, we can still take them into account by using an average/typical buildup of that wall type. More information can be found in Revit guide Paragraph 7.2.
Start now with BIM & LCA
Learn how to integrate BIM and LCA for quick and accurate assessment of your building's environmental impacts.

Academy
One Click LCA X Autodesk Revit course
Learn how to use the One Click LCA integration for Autodesk Revit, how to overcome common challenges in BIM/LCA integration and how to use the integration to optimise your design and monitor embodied carbon throughout the design process.


Contact our BIM experts & book a demo
Learn more about One Click LCA Revit integration and how it can support your projects.